Fisiología de la mastoides: aviso a los cirujanos
Insights in the phisiology of the mastoid bone: message to the surgeon
ENT Department – University Hospital Antwerp and Temporal Bone Foundation, Brussels Avenue du Polo 68 B-1150 Brussel Belgium (BA, NCP) Laboratory of BioMedical Physics – University of Antwerp Groenenborgerlaan 171 B-2020 Antwerpen Belgium (JD, JB)Bernard Ars, Joris Dirckx, Nicole Ars-Piret, Jan Buytaertmacs-Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(2) 296-310
To reach the temporal bone, surgeons often consider making access through the mastoid. It is, however, imperative that the surgeon is aware of the mastoid’s morphology, physiology, its functional parameters and the implications of damaging or altering this structure.
We review established findings on the developmental and functional morphology, and the delicate pressure balance variations in the middle ear cleft. Then, an overview is given of the possible surgical access methods for the temporal bone through the mastoid. We look for implications of each procedure, which can only be understood through the knowledge of the preceding outline, so that surgeons can justify a certain surgical approach.
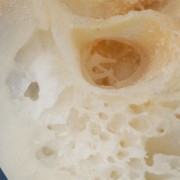
El EMA y el sistema de aireación mastoideo (MACS)
Tesis Doctoral -Victor Slavutsky ( ver EMA.Implante Coclear.Pgs.10-12)
Siguiendo la filosofía conceptual de este abordaje y su respeto por los tejidos sanos, el EMA a diferencia de los abordajes transmastoideos preserva y no destruye el Sistema de Aireación Mastoideo (MACS), que permite la difusión de gases ,mantener la temperatura y la presión del oído medio.
Este artículo complementa el anterior y demuestra la importancia del MACS en la cirugía de la mastoides.
El EMA es el abordaje que mejor conserva este Sistema de aireación del oído medio,con la técnica semiabierta (ver Colesteatoma)